The humble Solid-State Drive, or SSD as it’s more commonly known, has become a mainstay in modern technology despite initial fears that the cost of the product could see it always sit as a premium add-on. Fortunately, as time advanced, so did technology and manufacturing methods. We are now in a space where SSDs are the standard option for storage in laptops and PCs.
All the best laptops and PCs will now use SSDs, but despite their popularity and importance to how your devices run, you might not know exactly what it is or how it works. With archaic mechanical hard drive starting to phase out, here’s everything you need to know about SSD technology and why it’s here to stay.
What does an SSD drive do?
An SSD drive is, in basic terms, where you store the data from your PC or laptop. It uses flash memory which is what makes it a faster solution compared to mechanical hard drive disks. Traditional hard drives consisted of moving parts and this means is that when data was being stored or transferred, it would be a much slower and louder process.
An SSDs ability to use flash memory is a major advantage but also the cost of producing the product prevents larger storage sizes from being widely available at this time. Everyday use laptops, including Chromebooks, will typically start with anywhere from 64GB to 512GB of SSD storage whereas premium options like gaming laptops or creative use laptops will go as far as 2TB. Some products would use an SSD to store the operating system on and leave a small amount of storage free for use while also having a mechanical hard drive installed for alternative storage but this typically seen in budget laptops or PCs now.
SSDs can be internal, having been installed by the manufacturer or yourself. They can also be purchased to use as external storage if you want to keep something mobile and interchangeable between devices.
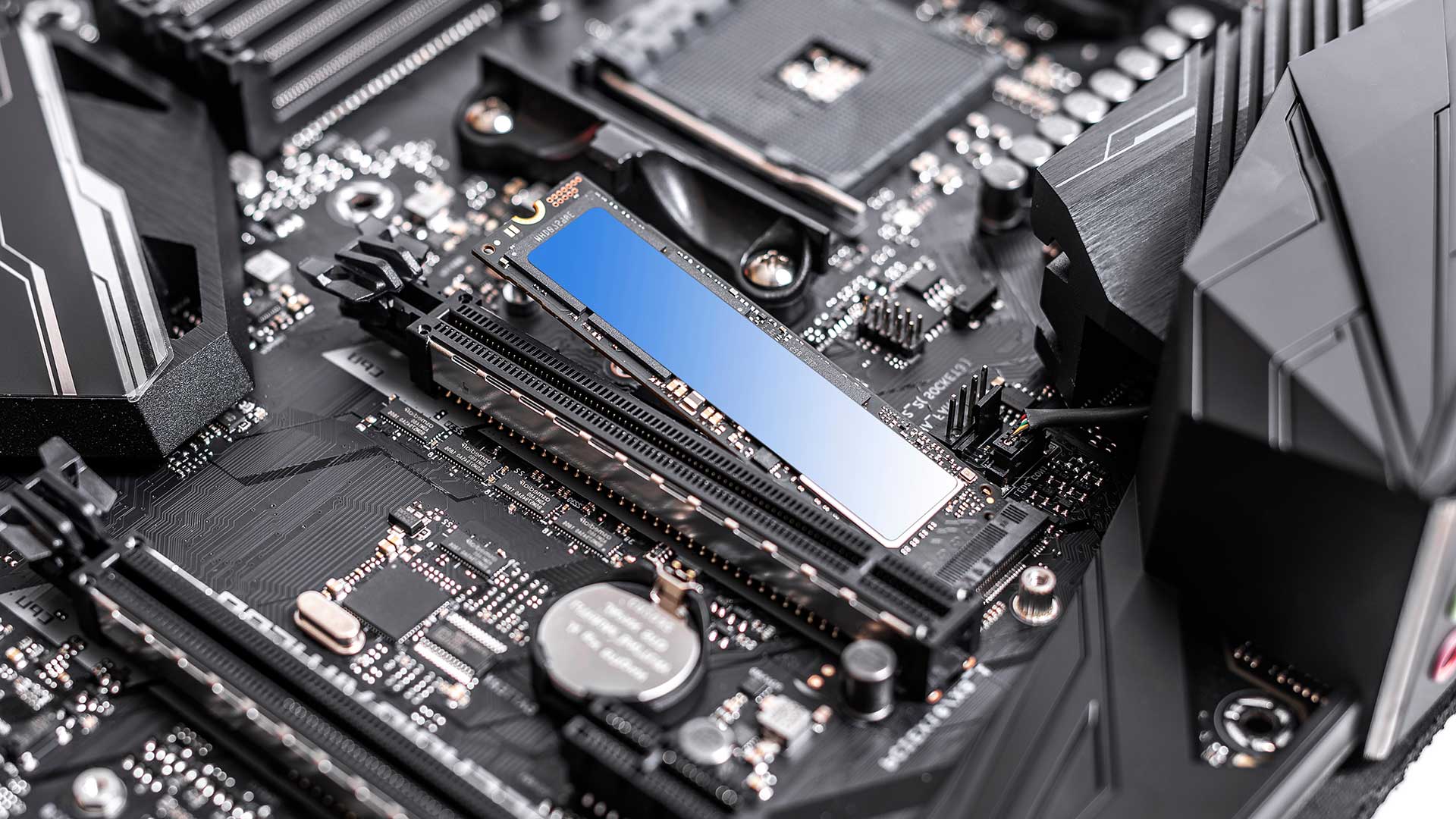

What are the different types of SSD?
If you are looking at the specifications of laptops or PCs, you might notice that there are a combination of different letters that follow some SSDs. There are different types of SSD and it usually refers to the way that the SSD is connected to the motherboard.
SATA, mSATA and older SSDs
The SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) SSD is slowly being phased out as it is limited to speeds below 6Gbps. Newer technology is also just easier to install and fit into modern motherboards.
NVMe and PCIe SSDs
NVMe (Nonvolatile Memory Express) and PCIe (PCI express) are the most up to date and future-proofed SSDs on the market. They are capable of a higher bandwidth and lower response rate, truly increasing the efficiency of your laptop or PC. They can run at speeds up to 16Gbps.
